Hello everyone! 🙂🙂🙂 Welcome to The DevOps Diary.
The DevOps Diary is a blog dedicated to sharing insights and experiences in the world of DevOps, with a focus on best practices, tools, and tips for improving software development and deployment processes.
As an engineer with years of experience, I’ve encountered a lot of challenges and learned a lot of valuable lessons. I started this blog to share my experiences with others and help them navigate the world of DevOps more effectively.
So.. Let’s get started 🥂
- About Server
Today we’re talking about servers and virtualization. Before diving into the technical world let’s try to understand the basics with a real-world example.
Let’s say you own land (1 acre) and you’re constructing your dream home. You and your family live with plenty of space. But look at Picture-1, there is lots of empty space. So using 1/4 of the land, you build a new house to rent. You still have the same space to live with your family but now you’re also making a passive income (Picture-2).
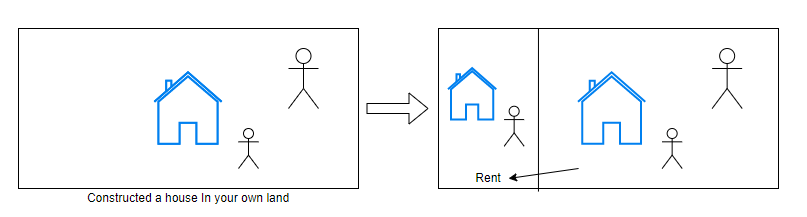
Picture-2 is more effective than picture-1.
When we’re talking about DevOps, improving efficiency is a goal. So here it is.
– – – – – – – From the Web – – – – – – – –
In computing, a server is a piece of computer hardware or software that provides functionality for other programs or devices, called “clients”. This architecture is called the client–server model.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – — – – – – – – – – – –

Let’s say you have a website that you want to make available to people all over the world. You can’t just store the website on your personal computer and expect it to be accessible to everyone. Instead, you can rent space on a server (hosting) from a company that specializes in providing servers for websites. That way, your website can be stored and managed on the server. Like google.com, amazon.com, etc. these things are in a public server. That’s why you can access them. So that’s nothing but a server.
According to the above home-land real-world example, let’s say demo.com buys five servers for the organization. Each and every server contains 100GB of storage and 100 cores.
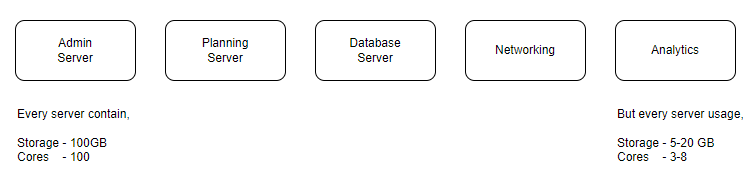
However, the departments do not end up using the entirety of the resources available. So it’s a resource waste. Inefficiency is a challenge and a company wide issue.
That’s how Virtualization comes into the picture.
- About Virtualization
– – – – – – – From the Web – – – – – – – –
In computing, virtualization or virtualisation is the act of creating a virtual version of something at the same abstraction level, including virtual computer hardware platforms, storage devices, and computer network resources.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – — – – – – – – – – – –
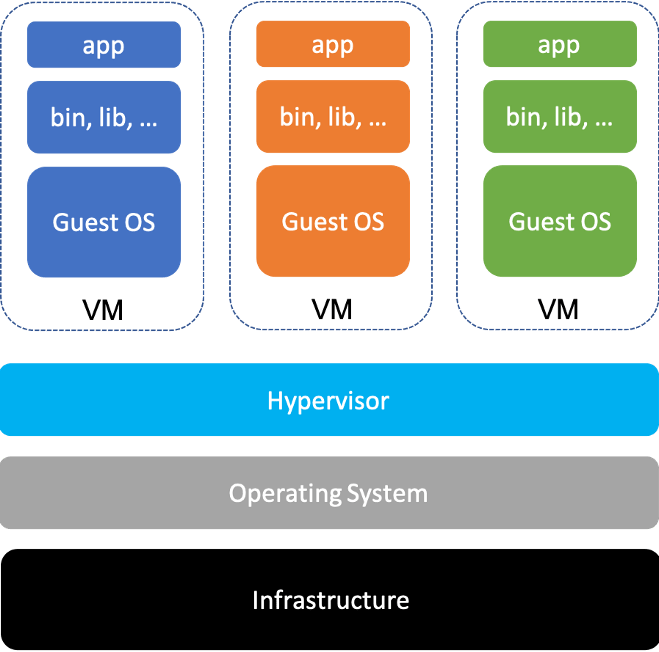
Virtual Machines are nothing but a virtual environment which functions as a virtual computer system and have their own CPU, Memory and their own Hardware.
Hypervisor is the software that can install virtual machines(VMs) on your bare metal or a physical server.
Here we’re not physically breaking the partitions. It’s called Logical Isolation. So now we can name these as VM 1, 2, 3, …
I would like to give you some popular VMs.
- Oracle VirtualBox: This is a free and open-source VM that can be used on Windows, macOS, and Linux. It supports a wide range of guest operating systems and can be used for the development, testing, and deployment of applications.
- VMware Workstation: This is a paid VM that can be used on Windows and Linux. It supports a wide range of guest operating systems and can be used for the development, testing, and deployment of applications.
- Microsoft Hyper-V: This is a free VM that is built into Windows Server and Windows 10. It can be used for the virtualization of Windows and Linux guest operating systems and is often used in enterprise environments.
- Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2): This is a cloud-based VM that is provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It can be used for the virtualization of a wide range of guest operating systems and is often used for hosting websites, running applications, and storing data in the cloud.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Compute Engine: This is a cloud-based VM that is provided by Google Cloud Platform. It can be used for the virtualization of a wide range of guest operating systems and is often used for hosting websites, running applications, and storing data in the cloud.
- Docker: This is a container-based virtualization platform that can be used for running applications in a lightweight and portable way. It is often used for developing and deploying microservices-based applications.
Next, we’ll talk about containerization. 🎉🎉🎉
Was this guide helpful for you?